Not sure what a 302 redirect is or when to use them? Are you curious about the impact on your SEO efforts?
I’ve got good news: 302 redirects are actually pretty simple. At its core, a 302 redirect is a way to tell search engines and users that a page has moved temporarily and to direct them to a new page for a short period.
Simple enough, right?
The problem is using the wrong redirect can significantly impact SEO and user experience. This is why getting the redirect right is crucial to your overall digital marketing strategy.
So what’s the difference between the types of redirects, and when should you use a 302? Here’s what you need to know.
What’s the Difference Between a 302 Redirect and 301 Redirect?
A 302 redirect is an HTTP response status code that tells search engines a page has moved, but only temporarily. It then directs users (and search engines) to the new, temporary page.
A 301 redirect is a server-side HTTP response status code that tells users and search engines a page has permanently moved, and it won’t be coming back.
For users, there’s little difference between the two types of redirects. They get sent to a new (hopefully more useful) page regardless of the redirect type.
The core difference between a 302 redirect and a 301 redirect is the amount of time the redirect is in place, but a 302 also leaves something important behind: link equity and page rank.
When you use a 302 redirect, the original page usually maintains its Google ranking, so it shouldn’t impact your SEO efforts. However, a 301 redirect causes the original page to lose ranking and can cause it to be deindexed by search engines.
According to Google, the main reasons to use a 301 (permanent) redirect are:
- You’ve changed domains
- People access your site through multiple URLs
- You are merging two websites or pages
You might also use a 301 redirect when switching from HTTP to HTTPS or when you merge two related pages. Any time you move a page and have no intentions of bringing it back, use a 301.
When you use a 301 redirect, the original page is no longer considered by Google, which is the main reason you want to ensure you use the correct type of redirect.
Say you’ve spent years establishing a pillar content page to rank for a key term in your industry. You decide to take the page down for a few days to redesign and update the page. If you use a 301 redirect, Google thinks the page is gone forever and removes the page from indexing.
Ouch.
Use a 302 and Google knows the page is coming back.
The type of redirect you use severely impacts your SEO, so make sure you always use the correct type for the situation.
Four Reasons to Use a 302 Redirect
So, what are the exact benefits of using a 302 redirect? Not all redirects are created equal, and using the wrong redirect can have a severe impact on your site’s SEO, as we’ve already covered.
Remember, a 301 redirect is permanent. You are telling Google and users that the page is gone and will never return. If the change is not permanent, you’ll want to use a 302 redirect.
Here are a few benefits of using a 302 over a 301 redirect.
302 Redirects Improve UX
Few things are more frustrating than clicking on a link and not finding the content you expect. It’s enough to send most users back to the search results (and to a competitor).
A 302 redirect makes sure users and search engines always find the content they are looking for. For example, if a product is temporarily out of stock, you might use a 302 redirect to send customers to a related product page or a page letting them know when the product is likely to be back in stock. You might also use a 302 to send users to related content while you redesign a pillar content page.
302 Redirects Are Temporary
Unlike 301 pages, 302 redirects are temporary, which means you can switch back at any time. This provides a lot of flexibility for site owners. For example, you could temporarily send site users to a related page while you redesign a landing page.
Because the switch is temporary, Google won’t remove the page from search results or otherwise devalue the page in its ranking.
302 Redirects Shouldn’t Hurt Your SEO
A 302 redirect tells Google (and all other search engines) that the move is temporary and preserves the page’s ranking and link equity. As a result, implementing the redirect shouldn’t impact your SEO. That means all your hard work won’t be in vain!
When the page no longer needs to be redirected, simply remove the redirect, and your SEO shouldn’t be affected.
302 Redirects Are Easier to Implement
Creating a 301 redirect requires access to your server, which means most digital marketers and site owners have to enlist the help of a developer to implement a 301 redirect. 302 redirects, however, can be created relatively easily using meta tags or a WordPress plugin. That means you can quickly implement them and easily take them down.
Note: Do not use 302 redirects when permanently moving a page just because they are easier. If a page move is permanent, always use a 301 redirect. Depending on your site, 301 redirects might be easy enough to create. If you aren’t sure where to start, head to your host’s knowledge base or look for a WordPress plugin.
When Should You Use a 302 Redirect?
Remember, the core difference between 301 and 302 redirects is the permanency of the move. If you are moving a page for a short time, you’ll want to use a 302 redirect to preserve the original page’s integrity (and ranking).
Let’s look at a few examples of when you’d want to use a 302.
When a Page Is Moved Temporarily
A 302 redirect makes no practical difference for users. They still get sent to the new page regardless. For search engines, however, the temporary nature of the switch is crucial.
Essentially, you are telling search engines, “Hey, don’t worry about this page right now; the other page will be back soon.”
If you are confident the move is temporary, 302 is the way to go. For example, you might move a page temporarily because:
- You are updating the page, but the new page isn’t live yet
- You’re looking to get feedback about a new page before moving permanently
- You’re running a time-sensitive promotion and want to redirect visitors to the page for a short time
When a Page Is Under Development
Another reason to use a temporary redirect is when a page (or website) is under development. Extensive redesigns might require taking your site offline, which can be frustrating for users and confusing for search engines.
Rather than leaving users hanging, a temporary redirect lets them know the page or site will be back very soon.
In this situation, you might send users to an email sign-up page or to offer a countdown clock so they know when the site will be back. Here’s an example of a countdown page from Themeforest with a countdown clock:

The page also offers links to social media accounts to help build a social media presence.
When the Content Is Inactive or the Page Broken
You might also use a 302 redirect when a page is broken or inactive. You don’t want users to land on a blank page (or get a 404 error), so a temporary redirect may be the way to go. Remember, only use a 302 if you plan to bring the page back.
For example, the content might be inactive because you run a semi-annual sign-up period for a membership site or you have a landing page for a recurring webinar that’s currently unavailable. A 302 should ensure the site maintains its SEO ranking and is ready to go when you want to reactivate the page.
When a Product Is Unavailable
Think about the last time you tried to order an item online, only to find out the product was no longer in stock. You were so close to having that item in your hands, only to find out it’s gone, and you have no idea when it might be available again.
It’s frustrating, and you’re likely to head to a competitor to complete your purchase. This is why stockouts (when a product is out of stock or unavailable) can hurt overall revenue and impact brand trust.
The reality is, items will sometimes go out of stock. It’s just part of doing business. A manufacturer might run out, or the supply chain might otherwise be impacted by something out of your control.
While you might not always be able to control stockouts, you can use redirects to preserve user experience. For example, you might use a 302 redirect to send users to a waitlist page, like this one:
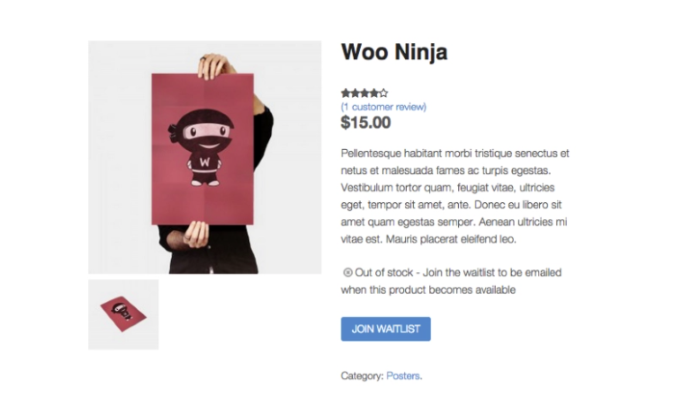
You could also send users to a related product (just be sure to let them know!). When the product is back in stock, you can reactivate the original page and preserve all that SEO you worked so hard for.
When A/B Testing Content or Design
Whether you are in e-commerce, the service industry, or run a local business, A/B testing is crucial to your bottom line. A/B testing allows you to test two different versions of the same page to see which version drives conversions, sales, or any other behavior you want users to take.
For example, I used A/B testing to figure out which CTAs to use in the sidebar of my website.
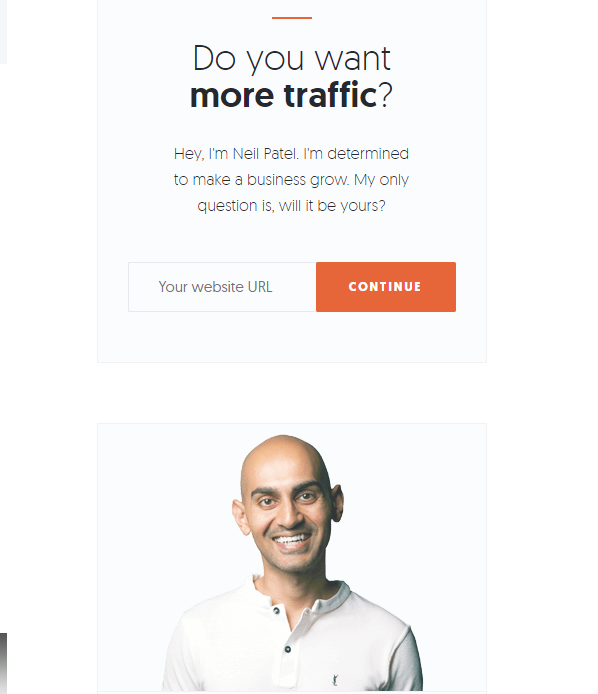
It turns out, the orange button converted much better than other colors.
Here’s another example of the power of A/B testing: WallMonkeys, a company offering wall decals and murals, increased conversions by 550% by using A/B testing to figure out what site users were more likely to respond to.
So where do 302 redirects come into play?
Well, you don’t want to permanently redirect your page because you might find out the original page was the best! Instead, use a 302 redirect to temporarily send a portion of your users to the adjusted page without losing your ranking. When the test is over, you can remove the redirect and go right back to normal.
If you are struggling with A/B testing, check out this guide for creating a winning A/B testing strategy.
To Redirect to the Desktop or Mobile Version of Your Site
If you aren’t already offering a mobile-friendly website, it is past time to do so. Seriously. Google moved to mobile-first indexing in the summer of 2019.
Your site should already work well on both mobile and desktop, but there are some reasons why you might still have a mobile version of a website.
For example, a banking app might offer a streamlined version of their website for mobile users, or they might find most mobile users are looking for a branch location. A 302 can send those users to the most useful page. You might also use a streamlined navigation bar for mobile and allow desktop users to access the complete version.
In both cases, a 302 redirect ensures every user lands on the site most useful to them.
Conclusion
Redirects can get confusing: 301s, 302s, plus 404 errors for when pages are broken.
Navigating these can be a pain if you are not a developer or a technical SEO expert. Hopefully, I’ve helped you better understand when and why you’d want to use 302 redirects on your site.
Here’s the TL;DR version: 302 redirects are temporary and generally preserve the SEO of the original page. 301 pages are permanent and tell search engines to disregard the old page in favor of the new page.
Now that you understand the difference, make sure to implement the right one on your site.
Have you used a temporary redirect before? What challenges did you face?
The post The Most Important Reasons to Use a 302 Redirect appeared first on Neil Patel.


